All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents

Interact these problems to relevant task teams, follow with up until there's a remedy, and report the client resolution. Ensure that all jobs are following their budgets and distribution times.
Develop a system to strategy, track, and file every solitary program you take care of. At the very least 4-6 years of experience in program monitoring with IT tasks is important.
Advancement is nitty-gritty when it comes to the modern technology sector, and within that standard, there's a behind-the-scenes orchestrator guaranteeing every little thing runs seamlesslythe Technical Program Manager (TPM). This unrecognized hero plays a critical duty in the success of technology tasks, bringing order to chaos and guaranteeing that the gears of development turn efficiently.
What tools do I need to succeed as a Technical Program Manager Resume Tips?
It's a delicate dance in between setting ambitious goals and making sure assumptions remain securely based actually - technical program manager courses. program management for tech companies. It's not simply about creating a strategy; it's regarding implementing it flawlessly. TPMs wear the hats of both visionary coordinators and pragmatic administrators, ensuring that every action aligns with the overarching project purposes
In the large landscape of tech tasks, efficient interaction is the bridge that connects diverse teams and stakeholders. Here, TPMs radiate as adept translators, decoding the elaborate language of tech for non-technical stakeholders. They connect the gap, making certain that everybody, no matter their technological background, recognizes the project's objectives and progress.
They have the foresight to identify potential challenges, varying from unforeseen technical obstacles to outside factors past the team's control. TPMs establish strategies to reduce dangers, making sure that the project cruises via stormy weather condition with strength.
Below, TPMs take on the role of allocators-in-chief, purposefully distributing resources to maximize efficiency. From personnels to budgeting, they ensure that the job has the best individuals with the best abilities and the essential devices at every phase. Constant evaluation and adaptation are vital. As the job landscape shifts, TPMs reallocate sources dynamically, guaranteeing that the group stays active and responsive.
Why is a What Is A Technical Program Manager? critical in tech program management?
In a globe where technology is king, preserving high-quality requirements and stringent quality control is non-negotiable. TPMs, hereof, end up being the gatekeepers of quality. They set rigorous standards for every single component of the task, from code to design, making sure that completion item meets or exceeds the specified criteria.
TPMs develop a culture where quality is not simply a goal yet a habit, permeating every facet of the task. Via their careful oversight, they infuse confidence in stakeholders and add to the lasting success and reputation of the company. Being a successful TPM requires even more than simply a knack for job monitoring.
What tools do I need to succeed as a Top Technical Program Manager Jobs?
While TPMs may not be coding wizards, they need a strong understanding of the technical landscape. This includes familiarity with the technologies entailed, an awareness of market fads, and the ability to comprehend the ramifications of technical choices. Leading without authority is a TPM's superpower. They need to influence and lead groups made up of individuals from different divisions, each with their very own objectives and concerns.
In the technology world, problems are not roadblocks yet challenges waiting to be fixed. TPMs need a flair for creative analytic, believing on their feet, and adapting to unforeseen difficulties. TPMs are the communication nexus of a task. Whether it's conveying complicated technological information to a non-technical target market or fostering cooperation amongst employee, efficient communication is non-negotiable.
Strategic believing includes expecting challenges, picturing the project's trajectory, and aligning it with broader business objectives. As technology develops, so does the role of the TPM. Over the last few years, the landscape has seen a shift in focus from standard job management to an extra vibrant and flexible method. Agile has actually ended up being much more than simply a buzzword; it's a means of life for many TPMs.
, has come to be a keystone in the TPM's toolkit. In the age of huge data, TPMs are progressively relying on data-driven understandings to notify their decision-making procedures.
What are the requirements to become a Top Technical Program Manager Jobs?
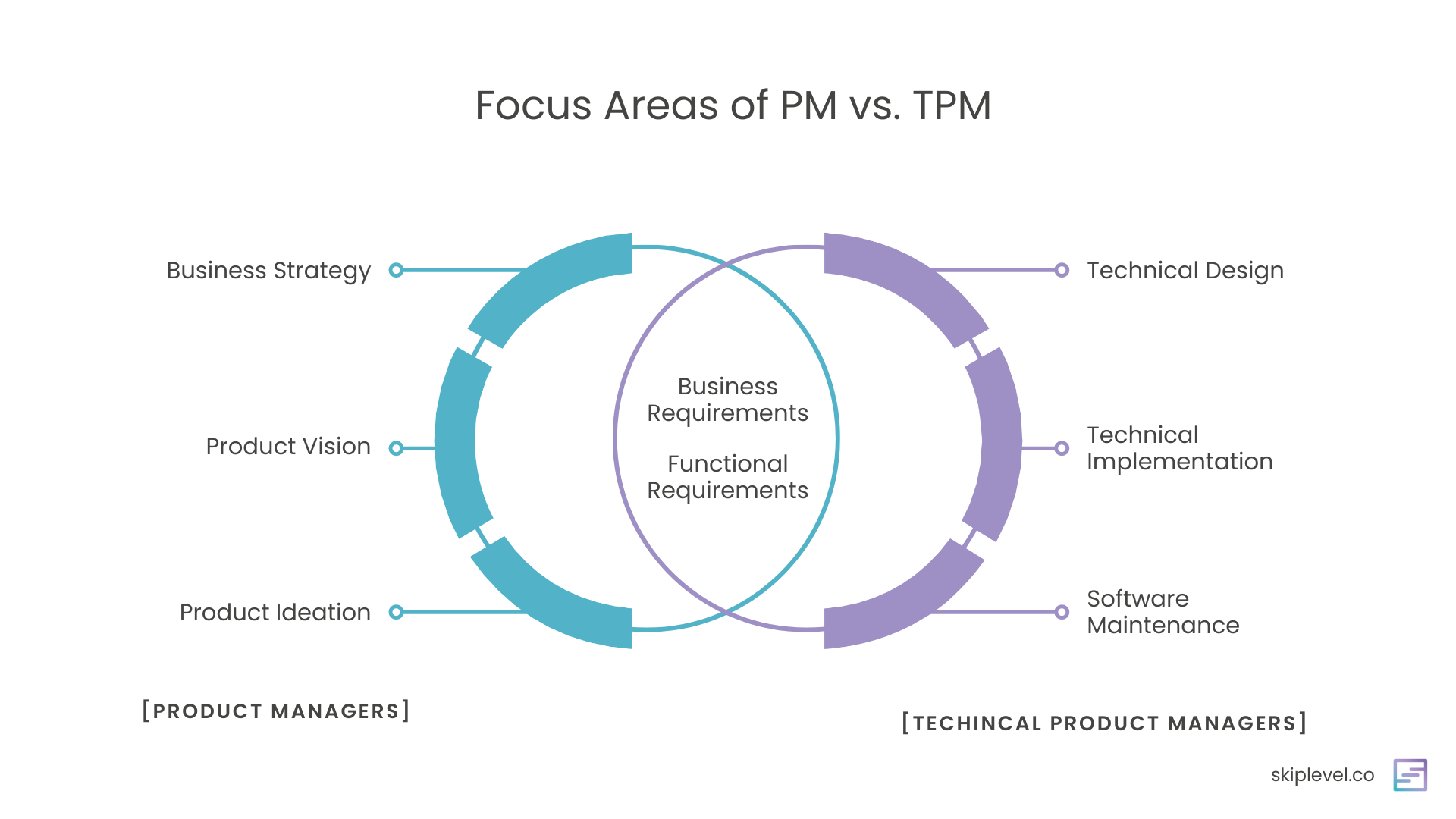
Unlike typical job supervisors, TPMs should deeply comprehend the technical aspects of the projects they take care of. This dual expertise allows them to interact with design teams successfully, understand technological challenges, and make sure that tasks are finished in a timely manner and within budget. Whether you're looking to work with a TPM or turn into one, understanding the duties and ability needed is essential for success in the tech sector.
The courses cover vital subjects such as job lifecycle administration, danger evaluation, resource appropriation, and software application growth processes. With a concentrate on real-world applications, our training ensures you are prepared to take care of the intricacies of technical jobs in any industry. Gaining a certification can dramatically enhance your job leads, demonstrating to employers that you have the expertise and skills needed to succeed in a TPM duty.
From startups to Ton of money 500 firms, organizations around the world are seeking qualified professionals to lead their technical programs. Whether you're looking to employ a TPM or are interested in TPM jobs, TPM Institute can aid you browse the work market and attach you with the ideal possibilities. Our programs are not almost learning; they are regarding launching your occupation in one of the most desired areas in the technology market.
Our are devoted to giving you with the most effective possible education, using insights based in real-world experience. They are dedicated to assisting you accomplish your accreditation and be successful in your job. For more details concerning our programs and accreditations, at Take the following step in your career with TPM Institute and become a leader in technical program management.
Technical Program Manager Salary
There's a propensity for people to move towards extremes when conceptualizing technological program supervisors. The truth is there is a spectrum of technical deepness amongst TPMs, and this often varies by project and customer.
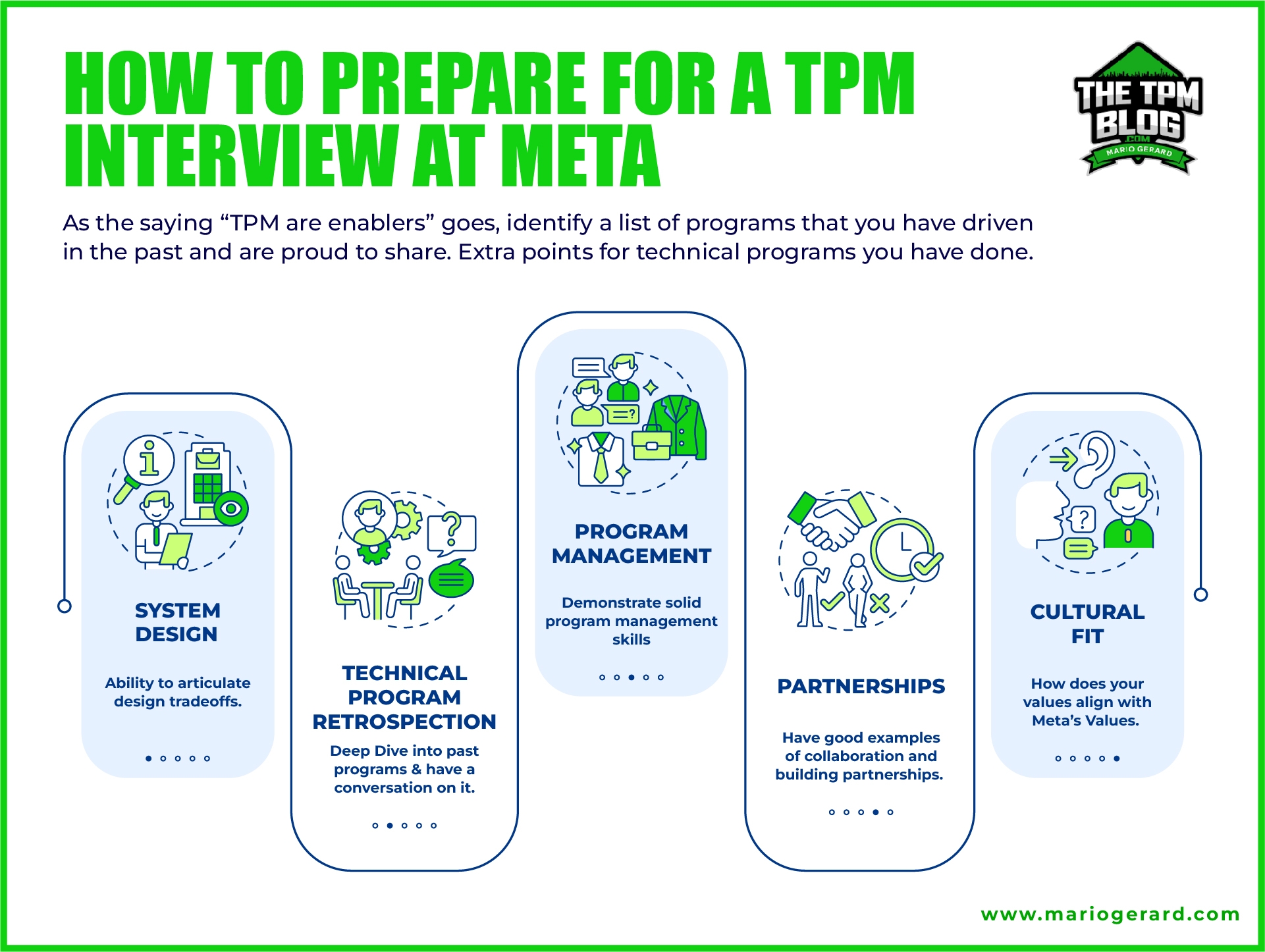
Securing a position at Apple or Netflix requires more than just coding skills—it demands targeted preparation and strategic insights. Resources like Two-Month Coding Prep Courses offer tailored coaching to help participants achieve career success. From coding bootcamps to mock interviews, these tools prepare candidates to excel
They can articulate intricate technical principles to non-technical stakeholders and assist in collaboration in between diverse teams. TPMs succeed at recognizing and fixing problems that emerge during task implementation, guaranteeing that projects remain on routine and within spending plan. They influence and lead their teams, cultivating partnership, advancement, and continual enhancement. TPMs' obligations can vary depending on the organization and the certain project they're working with.
TPMs function to guarantee that all staff member are functioning in the direction of the exact same objectives, avoiding miscommunication and wasted initiative. They anticipate and adjust to changes in task demands, making sure that projects can pivot efficiently when required. TPMs proactively address possible concerns, decreasing the chance of job hold-ups and failings. They motivate their groups to experiment with originalities and modern technologies, driving continual renovation and development.
TPMs work to ensure that all team members are working in the direction of the exact same goals, preventing miscommunication and lost initiative. TPMs proactively resolve potential problems, minimizing the probability of job delays and failures.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Best Leetcode Problems To Practice For Faang Interviews
The Ultimate Guide To Preparing For An Ios Engineering Interview
Software Developer (Sde) Interview & Placement Guide – How To Stand Out
More
Latest Posts
Best Leetcode Problems To Practice For Faang Interviews
The Ultimate Guide To Preparing For An Ios Engineering Interview
Software Developer (Sde) Interview & Placement Guide – How To Stand Out